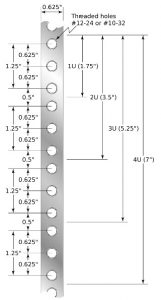
A “U” is a unit of measurement used to describe a rack. It lets you know the usable vertical space (height) available. Rack-mountable equipment is designed to fit multiples of U. For example, 1U = 1.75 inches, 2U = 3.5 inches… 40U = 70 inches.
Watch the Video Understanding Server Rack Dimensions: Ask a Bud Expert
Read more tips about specifying racks in our article, Practical Guidelines for Selecting Networking Enclosures.
Predictable, standard vertical hole spacing ensures all rack-mountable equipment can be mounted within racks. On a mounting rail, three holes are spaced 5/8 inches apart and the fourth hole is 1/2 inch from the third hole. These measurements are the distance from the hole centers. The pattern repeats for each U (1.75 inch unit). Each U begins and ends on the fourth hole.
Watch the Video Understanding Server Rack Dimensions: Ask a Bud Expert
Read more tips about specifying racks in our article, Practical Guidelines for Selecting Networking Enclosures.
Steel – Typically can be used in indoor or outdoor environments. It is corrosion resistant if powder coated or has a chemical conversion applied. Will absorb and conduct heat. Metal will dissipate heat better than non-metallic enclosures.
Stainless Steel – The corrosion resistance comes from nickel composition.
Die-cast aluminum – when molded it can be impact resistant.
Fiberglass – high impact strength and rigidity and has superior working temperature (-31 degrees F to 300 degrees F.) Good moisture and chemical resistance. Tends to be more expensive than polycarbonate but less expensive than other corrosion resistant boxes.
Polycarbonate (PC) plastic – Higher performance thermoplastic (injection molding.) The temperature range is less than fiberglass. It can be formulated to offer fire retention or UV stability and offers superior insulation. This can be offered in a clear material and is corrosion resistant. Polycarbonate objects weight less. If a polycarbonate object weighs 1 pound, a similar fiberglass would weigh about 1.5 pounds, aluminum 2 pounds, and steel 6 to 7 pounds.
ABS plastic – oLw-cost alternative for indoor applications where rating is not required.
For more material selection tips, read our article, NEMA Enclosures: Choosing the Right Material.
A: This is due to the draft angle which is required to eject the part out of the mold. If the enclosure walls were straight up 90 degrees, it would be difficult to remove the part from the mold.
A: Our colors were formulated exclusively for our company and its products for use with our equipment.
A: You can email one of our general sales service inboxes saleseast@budind.com or saleswest@budind.com. Please include a drawing, the quantity, and if there is a specific distributor you prefer to work with.
A: Two post racks provide one set of vertical rails to mount to. They are often used for telecommunication applications or other lightweight rack-mountable devices. Of course, they would typically be lower priced and also are easier to transport.
Watch the Video Understanding Server Rack Dimensions: Ask a Bud Expert
Racks date back to the 1800s, when they contained signal relays for railroad. In 1922, AT&T set the standard for their equipment racks at 19-inches-wide. Over time, 19 inches became the standard for all industries. A hundred years on, to fit large telecommunications equipment, the industry started using racks measuring 23 inches in width.
Read more tips about specifying racks in our article, Practical Guidelines for Selecting Networking Enclosures.
A: Powder coating is an environmentally safe alternative to wet paints. The finish is consistent and free of drips or runs which can occur when using liquid paint. The powder (paint) is negatively charged by the paint gun as it is sprayed and will adhere to the grounded metal part to be coated like a metal rack or box. The part is then cured in an oven. We utilize an IR oven. As the powder loses its charge in the oven, it begins to melt to the surface.
A: Bud has touch up paint available for sale that does a very good job of repairing the finish.
A: Bud’s enclosures are only truly UL rated when they are in the original designated form. Any additional cutouts or shifts in material could cause you to have to recertify the product. UL has stated that by utilizing an initially UL rated box, and UL components (like LCD screens, connectors, and switches,) the UL approval process for your end product will be much easier.
To test your product, you will need the Bud standard part number, and our UL file number (E194432) and give to UL. The majority of UL listed products in Bud’s line are under our file number. If a part does not appear under our file number, please contact Bud directly to request additional information. We would be happy to assist.
A: Modifications can be:
Watch the Video Discover the Quick Steps to 5-Day Delivery on Modified Enclosures
Want more modification tips? Read our article, How to Modify Enclosures to Get the Design You Need for Less time and Cost.
A: Within a hole pattern, Bud can hold to +/- 0.005” between machined features and +/- 0.030” relative to the enclosure edge (measured from the bottom right ) relative to a center line we can hold +/- 0.015”.
When adding Digital printing Bud can hold +/- 0.060″ from the bottom right edge of the printed surface.
Watch the Video Discover the Quick Steps to 5-Day Delivery on Modified Enclosures
Want more modification tips? Read our article, How to Modify Enclosures to Get the Design You Need for Less time and Cost.
A: There is not a minimum modification quantity if we are doing things like cutting holes, painting a standard color, installing PEMs or other basic modifications. If you are changing the material, doing a custom powder color, or changing the sizes of a formed box, then tooling or minimum buys may be in place due to our raw material supplier. Please note that while Bud can do customization in as little as one piece, costs could be more expensive based on individual set ups.
Watch the Video Discover the Quick Steps to 5-Day Delivery on Modified Enclosures
Want more modification tips? Read our article, How to Modify Enclosures to Get the Design You Need for Less time and Cost.
A: While we are happy to review all custom requests, most enclosures do not need to be fully custom. Standard products are routinely modified with cutouts, holes, and slots as part of our 5-Day Modifications program, the fastest in the industry. In addition, we offer digital printing or silk screening, special colors and finishes, shielded gaskets, and pre-assembly. Read more at https://www.budind.com/electronic-enclosure-modifications/
Watch the Video Discover the Quick Steps to 5-Day Delivery on Modified Enclosures
Want more modification tips? Read our article, How to Modify Enclosures to Get the Design You Need for Less time and Cost.
A: Bud offers our products through a large network of distributors throughout North America and internationally. You can find a list of our franchised distributors on our website: https://www.budind.com/find-distributors .
A:The bottom plates are an accessory, as some only need five sides for their application.
Aluminum Chassis Series
A: Anodizing is used to isolate, while iridites and chromates are used to retain electrical conductivity. Anodizing increases resistance to wear or corrosion of the product.
A: You can find a list of your local sales representative by clicking here: https://www.budind.com/representatives.shtml. If you have any questions, feel free to contact Bud’s sales department and we can assist you.
A: This information, and other data about our offering has been compiled at https://www.budind.com/BudRoHSList.htm
A custom electronic enclosure is completely developed from scratch and is used most often when a suitable solution cannot be found off the shelf. This allows for a very specific visual look of the enclosure as well as exactly meeting the needed dimensions and functionality.
A modified enclosure is a standard, off-the-shelf enclosure that has features or functions added to it. The most common modifications are made to enclosures by cutting holes, slots, or cutouts. Other modifications include digital printing, special colors, adding UV protection, and pre-assembly.
Read the full story in our article, Do I Need a Custom Electronics Enclosure?
Watch our video: NEMA Enclosure Ratings: How Well Can the Box Protect Your Components?
Terms like “waterproof” and “dust proof” are ambiguous. Is an enclosure merely rain-proof or is it fully submersible? Does it merely protect against intrusion by objects (such as fingers), or is it so tightly sealed that it’s airtight?
To clarify this situation, the National Electrical Manufacturer’s Association www.nema.org developed a clear set of standards called NEMA ratings. The ratings make it easy to specify enclosures with the appropriate level of protection.
Notifications